Full length human IgG antibodies are composed of 2 regions, the N-terminal region of each chain corresponding to the Fab (fragment for antigen binding which contain the variable regions and the CDRs) and the C-terminal region corresponding to the Fc (crystallizable fragment)
Until some years ago the scientist
focus mainly their efforts in the optimization of the Fab regions to develop
antibodies with highest antigen affinity and lower immunogenicity.
In the last years, especially with the
emergence of bispecific antibodies, e.g T-cell engagers there has
been a growing interest in modifying the Fc region to modulate
(enhance or remove) the antibody effector function.
The Fc region is able to bind with high
affinity the Fc gamma receptors (FcγRs), and the neonatal Fc receptor
(FcRn) expressed in the surface of the immune system cells (Reference) by triggering different effector functions such as
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) and antibody-dependent
cellular phagocytosis (ADCP) and complement- dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) responses (Reference)
Among the four subclasses of human IgG (IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4), which differ in their constant regions, particularly in their hinges and CH2 domains, IgG1 has the highest FcγR-binding affinity, followed by IgG3, IgG2, and IgG4. As a result, different subclasses modulate in different way the different responses ADCC, ADCP and CDC. (Reference)
In in the first generation of
monoclonal antibodies the Fc activity was modulated by producing of the
antibody in different Fc format on the basis of the antigen properties and the MoA
(mechanism of action) that they would confer to the antibody:
Blocking antibodies that do not have to activate the immune response where produced in the IgG4 format
For example Nivolumab which binds to the PD-1 receptor located on the cell membrane and inhibits its interaction with its ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. Since PD-1 is expressed on activated T cells, NK cells, regulatory T cells and B cells. Nivolumab has been desinged to block the interaction with the PD-L1 and PD-L2 and therefore releases immune cells from pathological immune suppression, but not activate the immune-response against these immune-cells otherwise we will obtain the unwanted depletion of effector cells inducing serious adverse events..
On the contrary, mabs targeting antigen expressed in the surface of cancer cells (e.g Cetuximab targeting EGFR) were produced in igG1 form to activate the immune-response against those cells and induce cell clearance. In fact, it has been demonstrated in preclinical models and ex vivo studies that target-bound cetuximab IgG1 isotype mAbs stimulate natural killer (NK) cell–driven cytotoxicity against tumor cells coated in mAbs via the interaction of the constant region and the CD16 receptor on NK cells
More recently igG1-Fc sequence engineering were largely exploited to further improve the modulation of Fc function:engineering as well as CHO cell line
Fc Function enhancement:
It is well-known that this effector function is modulated by the N-linked glycosylation in the Fc region of the antibody (N297 of IgG1).
In particular, absence of core
fucose on the Fc N-glycan has been shown to increase IgG1 Fc binding affinity
to the FcγRIIIa present on immune effector cells such as natural killer cells
and lead to enhanced ADCC activity.
As I reported in the ProteoCool Pills #10, the simple supplementation of the culture media with 2F-Peracetyl-Fucose allow to produce low fucosilated monoclonal antibodies in mg scale to be used for R&D screening, on the other hand, several strategies (as the GlymaxX® and POTELLIGENT® have been developed to build stable clones for large scale production based of afucosylated antibodies with improved therapeutic potency.
Since those cell lines may show some drawbacks in terms of
growth rate and mab productivity at the same time other scientists focus also
in the development of igG1 mutant (eg S239D/1332E named SDIE and G236A/S239D/A330L/I332E named GASDALIE – US patentUS20230057150A1 those similarly to afucosilated mab show improved affinity for the FcγRs even
in produced in the standard CHO cell lines.
In the past I had the opportunity to do some trials comparing
the ADCC activity (using the Promega ADCC assay, both F
and V versions) with using the igG1 WT afucosilated and igG1 SDIE mutant
(produced with standard fucosilation) for the same clone and interestingly (data not shown) it seems that their effect
could be combined at least from the results of this in vitro assay.
B) Fc Function silencing:
The
most recent alternative to the use of IgG1, which allow to point mutations in
the linker region between hinge and Fc domains were described to reduce or
fully abrogate Fcγ binding affinity and downstream effector cell activation
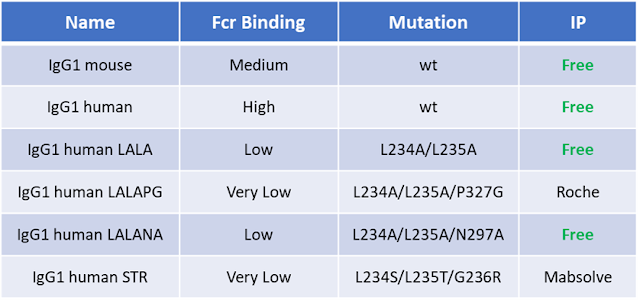
In
the following Table are reported some of the most known and used mutations:
From literature
the STR (recently developed by MAbSolve seems to be the only mutation that completely
abolish all the ADCC, ADCP and CDC activities (Reference) and it seems that STR do not alter the
antibody developability profile.
Even in this case I had the opportunity to do some R&D trials comparing the igG1 human wild type, LALAPG and STR mutants and I was not able to was not able to reveal meaningful differences between LALAPG and STR with the Promega ADCC assay (complete abolishment in both cases – data not shown) but this can be due to the fact that as shown in seems that the advantage of STR vs LALAPG is in the lower affinity of STR for the FcγRI which is probably more involved in trigger the ADCP than ADCC response or that the sensitivity of those kind of assay is not enough to detect so small differences (see Table3) the authors do not reveal any differences even in ACDP assays
I also performed antibody aggregation propensity detected
performing SEC on 10mg/ml samples subjected to different incubations (4°C,
37°C, Freeze/Thaw) and in this case the LALAPG seems to be slightly better
(data not show)
However, this post does not would provide any ranking or evaluation of the different mutants but just inform you about the possibility to test them to achieve the wanted MoA for your new monoclonal antibody.